On August 20, T-Mobile discovered that a hacker had gained personal information from unauthorized access to its system. Over 2 million of its 77 million customers were exposed.
Although T-Mobile quickly reported the incident to authorities, it's apparent that the cybercriminal is aiming to sell the data, including names, ZIP codes, phone numbers, email addresses, and payment information.
While it's still too early to determine the financial consequences T-Mobile will face from the incident, a recent study from UNC found that data breaches can cost companies as much as 3% of their market value. Dashlane estimates the average dollar cost at $7.35 million in the U.S., 60% of which is customer (revenue) loss.
What can business leaders learn from this incident to protect their teams and their customers going forward?
Lesson 1: Hackers Go for Weak Points, So Protect Yours
Understanding how hackers get in is the first step. There are four common ways that hackers access systems:
- Malware infiltration (placement of malicious software, including ransomware and spyware)
- Phishing (emails that trick recipients into giving away sensitive data or downloading a file that installs spyware)
- USB traps (a hardware device that contains a HID spoof)
- Mobile attacks (attacks specifically designed for mobile software)
In all cases, hackers look for the simplest vulnerability they can possibly use to compromise your system. That means they're not necessarily going to try to waltz in the front door. In the T-Mobile data breach, the thief was able to access the system through a hole in an API.
It's critical to plug your leaks. Since APIs run on web servers, they are available to all internet users. Like websites, hackers can crawl APIs.
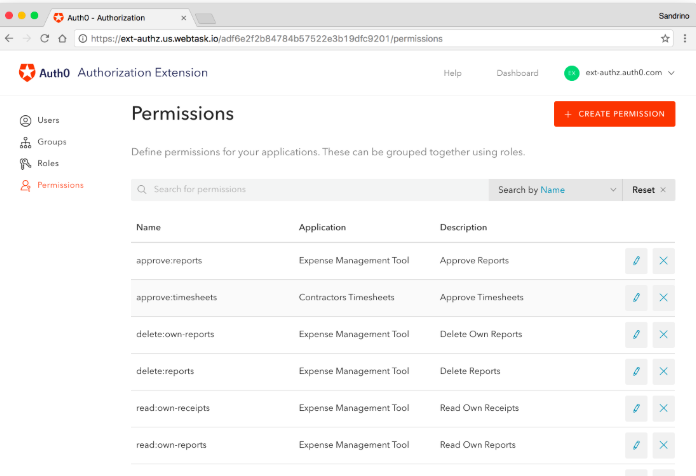
Authorize Your Users
To be sure you know who is working within your system at any one time, implement a strong user management system. You can build one in-house or outsource it. Many choose to outsource their identity management since the field is increasingly complex and time-intensive — a challenge for in-house teams to manage with the rest of their workload.
Auth0's user management dashboard, for example, lets administrators grant permissions for certain users to access sensitive customer information.
With this powerful web interface, they can add or remove users, modify their profiles, and identify any root-cause login issues.
With APIs, it's also important to remember to authenticate your apps in addition to authorizing users. You can use a standardized protocol for both authentication and authorization.
Lesson 2: Update Your Password Practices
A 2017 Verizon report found that 81% of hacking-related breaches were due to stolen and/or weak passwords. While for years teams relied on the MD5 (message-digest) algorithm to hash passwords (create mathematical representations of plain text), today it's not considered the safest method.
"A 2017 Verizon report found that 81% of hacking-related breaches were due to stolen and/or weak passwords."
Tweet This
Although originally MD5 hashes were designed to prevent anyone from working backwards from the hash to determine the real password, it's now possible to rapidly generate MD5 hashes to eventually find a matching password.
Evidence points to T-Mobile password hashes being MD5, which suggests the company may have been using outdated password practices.
To prevent the risk of password hacking, many providers are using bcrypt instead — a more resistant algorithm. bcrypt uses a salt, an additional layer safeguard for passwords in storage. Over time, users can increase bcrypt's iteration count to slow the process. This makes it more resistant to brute-force search attacks.
Implement Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication or 2FA is an alternative verification method. In addition to requiring users to type in a password, 2FA can also request a TOTP (a time-based one-time password algorithm) that it sends to the user's cell phone or other hardware device.
2FA can also require the second form of identification to be a biometric, such as a thumbprint or Face ID.
[Source]
While none of these solutions are foolproof, a second method of authentication has been found to prevent breaches in 80%of the cases.
Lesson 3: Improve Communication with Customers After a Data Breach
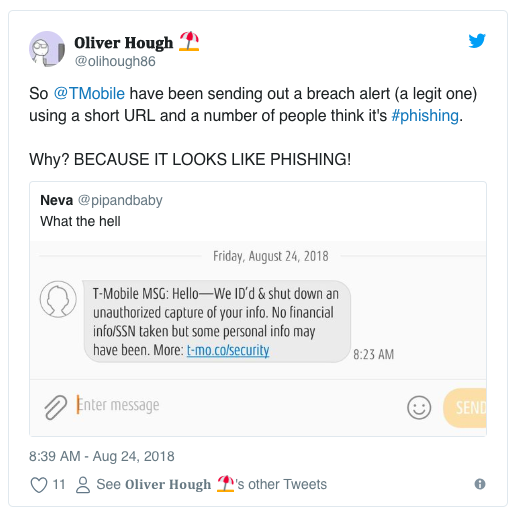
Although T-Mobile did attempt to notify customers whose accounts might have been compromised a few days after they discovered the incident, many of these recipients were put off — thinking the text message itself was a form of phishing.
[Source]
Texting can be a tricky form of communication for something so sensitive (particularly from a large, impersonal corporation). Organizations like Reddit and Equifax have succeeded with well-crafted PR campaigns and explanations on their websites:
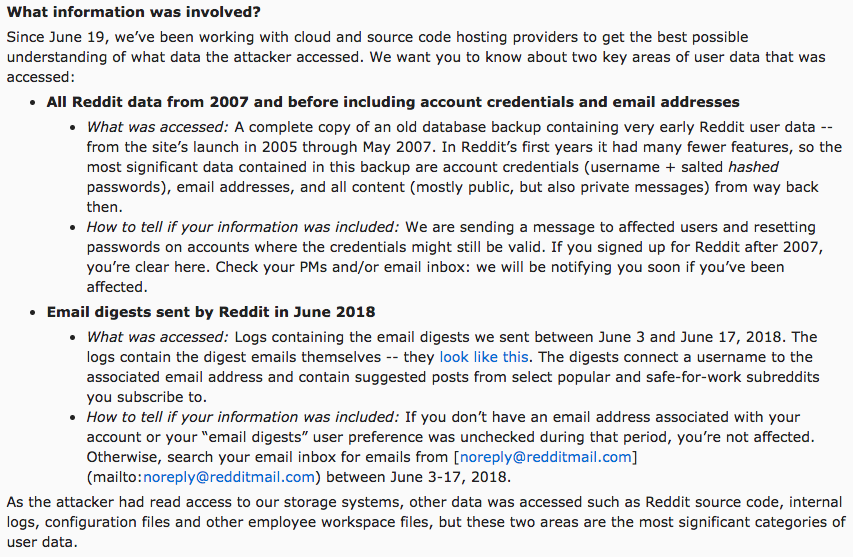
As a portion of the full announcement (which you can read here), Reddit clearly defines the scope of the breach, including details of what information the hacker accessed and how to know which users were affected.
Reddit also lets users know ahead of time that they will be contacting them through email to verify if their account has been compromised.
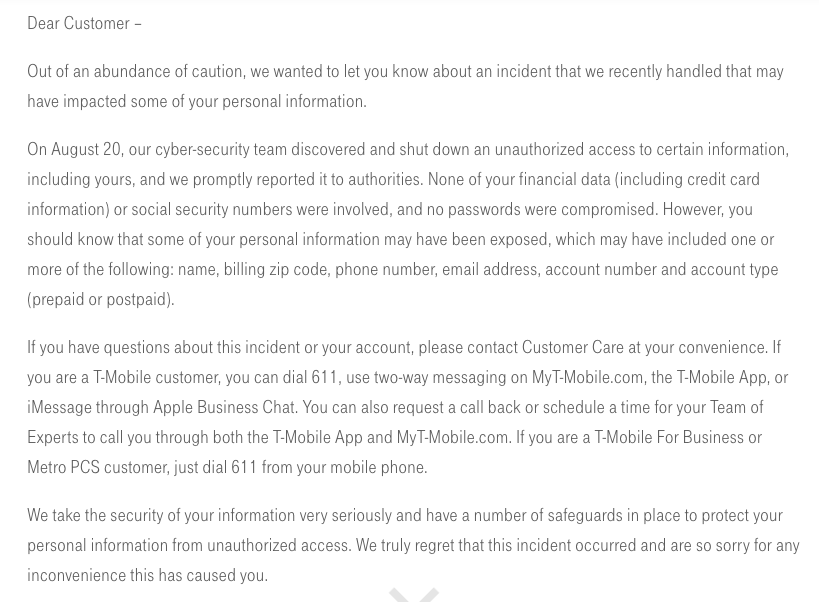
This is in stark contrast to T-Mobile's vague description that their team shut down “an unauthorized access to certain information.”
Being as specific and transparent as possible (as quickly as possible) will help your customers trust that you are handling the situation and keeping them safe.
Recent Data Breaches by the Numbers
It seems like every week there is a new catastrophe for personal data in the headlines. Reddit, Saks, Ticketfly, Panera, Lord & Taylor — these are just a handful of the major incidents so far in 2018.
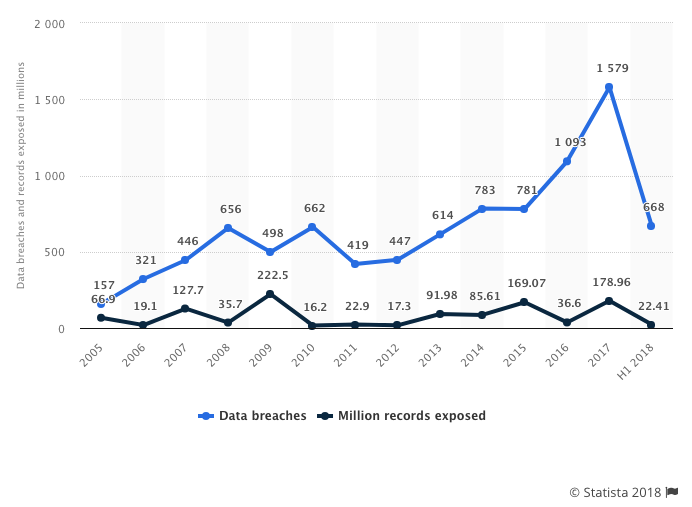
The first half of 2018 saw nearly 700 breaches, on pace to equal 2017's staggering 1,579 breaches.
The total number of exposed records from these incidents in the past five years tops 580 million.
"The first half of 2018 saw nearly 700 data breaches, on pace to equal 2017's staggering 1,579 breaches."
Tweet This
In addition to data breaches, data exposures — when data is improperly defended and open for access on the internet — are on the rise. Instead of a malevolent hacker getting through a protected system, a data exposure occurs if a database isn't correctly configured or doesn't require appropriate authentication. In 2018, Exactis, for example, exposed 340 million records, putting 2 terabytes of personal information at risk.
You don't have to be as large as T-Mobile to take powerful steps to secure your company. Small businesses, for example, can still implement multi-factor authentication and improve their password practices. Taking steps to secure your customer data — whatever your size — will help you avoid becoming an easy target for hackers.
Bolster Your Security in Order to Scale
Data breaches and exposures can quickly erode customer and investor trust — particularly at critical times in a business's lifecycle. For example, T-Mobile is currently in a $26 billion merger agreement with Sprint. The deal, which has already been subject to regulatory scrutiny, could face even more hurdles if parties see T-Mobile's lack of updated security practices as a liability.
On the flip side, if you strengthen your defenses and clearly communicate your progress, you have a better chance of emerging from any issues with your reputation intact.
Make sure you are on top of the latest security practices and protocol to avoid worst-case scenarios that could obstruct progress.