2018 will inevitably bring more and more sophisticated cyber attacks. As with all industries, the technology used continues to push the boundaries of what we previously thought was possible.
It continues to be critical that your company takes every precaution to protect itself. Knowing your users and managing their behaviors in your network are just some of the strategies you should employ in this increasingly complex landscape.
But if you, like many of your peer companies, have an IT team that is overwhelmed by alerts and competing demands, where do you begin?
The four tools below help you cut through the noise, quickly figure out where to focus your energy, and actively respond to suspicious behavior.
"Four tools to help you cut through the noise, quickly figure out where to focus your energy, and actively respond to suspicious behavior."
Tweet This
What Is Threat Intelligence?
The definition of threat intelligence continues to evolve as new threats emerge and multiply. In essence, threat intelligence seeks to recognize and understand the advanced tactics of cybercriminals and the particular ways in which they threaten data and networks.
Threat intelligence can be broken down further into five data types:
- Internal: Based on your team's own assets
- Network: Focused on your organization’s boundary
- Edge: Observes how Internet hosts are behaving at the edge of the network
- Open-source: Public blogs, Twitter and news feeds, and other chat channels
- Closed-source: Underground websites and information channels
The detailed nature of these definitions highlights the complex and evolving nature of the threat intelligence space. Best practices have evolved as in-house IT specialists work hard to keep up, but software tools also play a big part in helping organizations stay on the cutting edge. While threats have become more advanced, so have the defensive technologies that can help small- and medium-sized teams fight back.
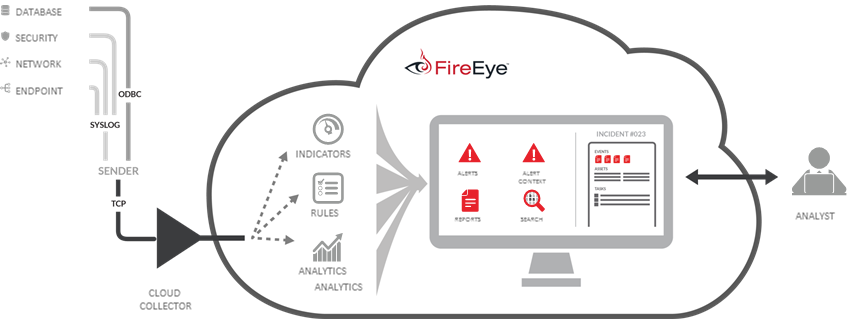
1. Threat Prioritization: FireEye
FireEye offers specific expertise in network boundaries — the delineation between the side of the network that a company privately owns and the public side that a provider often manages.
The core of FireEye's resources is its Threat Analytics Platform (TAP), which helps security teams prioritize among the multitude of alerts that arise. FireEye's platform allows IT administrators to quickly contextualize an alert and take action. TAP logs event data from a range of sources, such as security, database, network, and endpoint devices, and ranks them based on risk.
Alerts pass through FireEye's intelligence, including several rules that generate alerts. These are based on distinguishers (the type of action taking place) and frequency. If an action occurs repeatedly within a specific time frame, the combination of type and frequency will generate an alert.
FireEye also offers iSIGHT Intelligence Subscriptions and even an on-site intelligence analyst to help develop or complement in-house intelligence abilities. The company acquired cyber forensics firm Mandiant in 2014; together they developed a comprehensive set of services to develop and complement a company's existing threat intelligence capabilities.
Bottom Line: FireEye's threat analytics platform is helpful for teams that have existing security measures in place but have trouble distinguishing among alerts. TAP helps parse out and prioritize the real concerns.
2. Consolidated Management Tools: Palo Alto Networks
Palo Alto Networks takes advantage of shared threat information among its customers. Threat data from one customer will trigger automatic prevention mechanisms across its entire pool. As of January 2018, this included 48,000 customers in 150 countries. As Palo Alto Networks continues to expand, its protections become more widespread, helping limit the spread of any single attack overall.
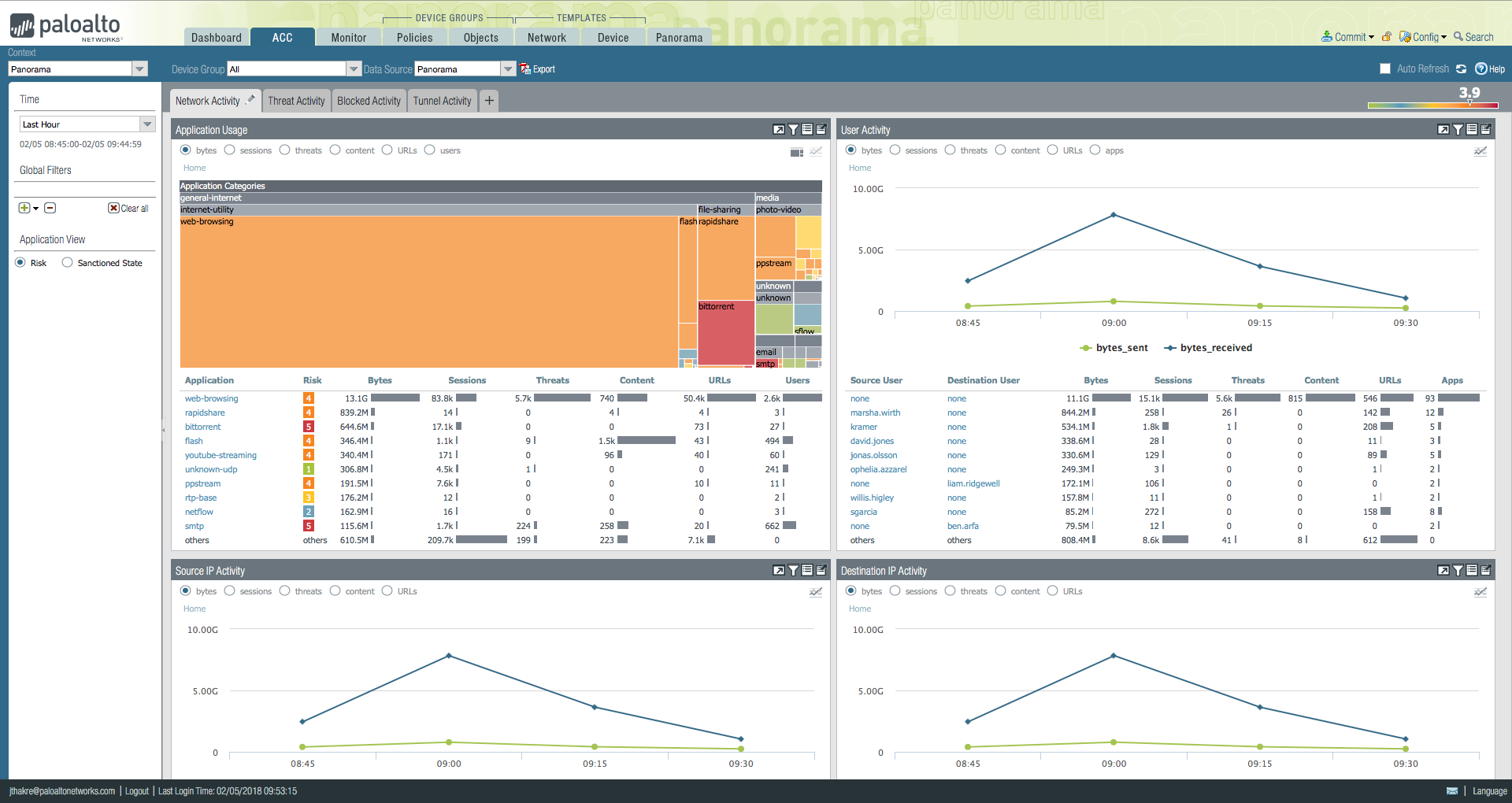
Threat intelligence sharing is one of Palo Alto's four cybersecurity pillars. A specific product for overwhelmed IT teams is its Panorama management tool. Panorama allows administrators to view traffic, manage device configuration, push policies, and generate reports from one console:
Teams have the option to toggle between a centralized dashboard along with more specific views, such as policies and objectives. In the Application Command Center (ACC) view above, an administrator can view network, threat, blocked, and tunnel activity, along with a graphical view of applications.
In Panorama each tab includes widgets to help visualize your network's traffic patterns. Administrators can build out custom tabs that focus on the information you want to prioritize, such as the activity of a user subset in a particular geography. The ACC also provides a comprehensive screen for historical (not just current) data.
Bottom Line: Panorama is a robust tool that allows IT teams dealing with a large volume of users and traffic to view all of its activity in real-time and develop and push appropriate policies to manage the flow.
3. Malware Search Engine: CrowdStrike
CrowdStrike focuses on securing endpoints; for the majority of companies, this is where its most sensitive data resides. If an endpoint is breached, cyber adversaries are able to easily move within your network and subtly take data for months without detection.
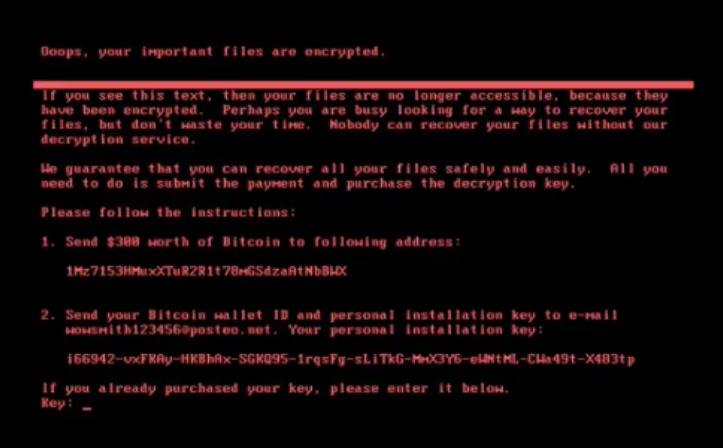
CrowdStrike recently released a malware search engine that allows teams to quickly understand threats as they arise. For example, if the following comes up on a screen, your team has all of the info it needs to begin an investigation:
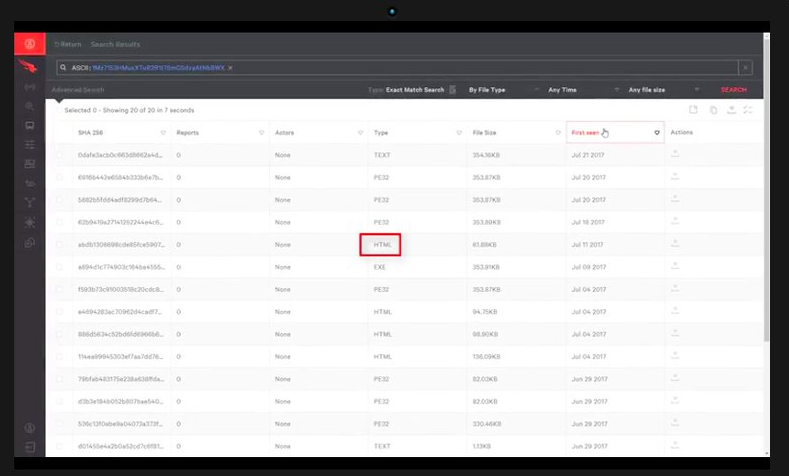
A malware researcher on your team can pick out peculiar pieces of text, such as the Bitcoin wallet ID in the first instruction, and enter it into CrowdStrike's MalQuery to yield matches in seconds:
The researcher is able to search malware in both metadata and binary forms and determine which returned files are executable. He or she can also see when the files were recently seen and download them for further investigation.
Historically, research tools have fallen far behind Google and other internet search options. It can take hours or days to really understand an attack. However, CrowdStrike's search engine amasses 50 billion security events worldwide every day, totaling 560 terabytes of malware. It is 250X faster than current search tools, allowing for powerful real-time search and less lag time before taking action.
Bottom Line: If your team is frustrated with figuring out the details of suspicious behavior, CrowdStrike's Falcon Search Engine can provide added speed and agility.
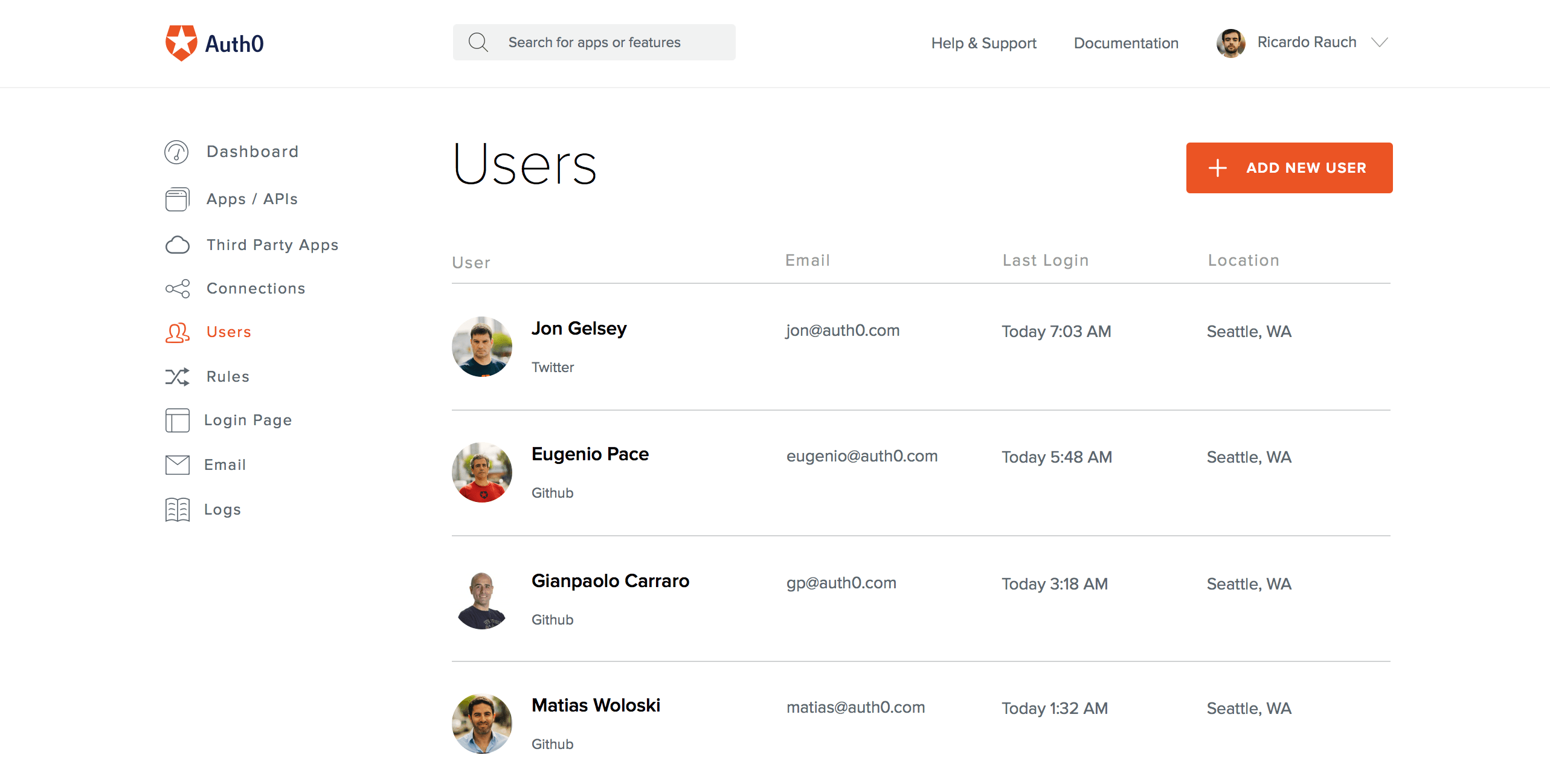
4. User Dashboard: Auth0
Here at Auth0 our team deals with complex identity use cases. We make sure that your company has the best insights into who your users are at any given time and how they behave in your network. To do so we have an extensible and easy-to-integrate platform that secures billions of user logins every month.
The platform provides:
- Single Sign On (SSO) capabilities
- Breached password detection
- Multifactor authentication
- Web and mobile app lock
- User management tools
- Passwordless log-in options
In particular Auth0's user management tool provides a centralized and actionable means of deeply understanding who is accessing your most secure data when — and from where.
Auth0's intuitive UX allows administrators to clearly see every relevant identity, along with rich user profiles. With Auth0 you can rapidly push rules like barring entrants with certain email addresses or collecting commonly used items, such as user credentials and URLs. You can deploy rules using GitHub, Bitbucket, and GitLab; they can be chained together or used individually.
Having this 360 view of your users allows you to detect any out-of-place behavior or unfamiliar users. The Dashboard offers you the ability to take swift action to highlight and block intruders if they enter.
Bottom Line: Auth0's user dashboard can help you understand your users at a granular level, including their pictures, personal details, locations, logins, and devices they use. Knowing users at this level, particularly if your company operates in the cloud, makes it clear when someone is out of sync and potentially a threat.
Don't Forget to Educate Your Employees
While all of these tools offer critical strategies and product enhancements to secure your company against advanced cybercriminal tactics, your most valuable source of rooting out and avoiding cyber threats is educating your employees. A recent study found that 91% of cyber attacks begin with a simple phishing email. Companies in the transportation, healthcare, and insurance sectors were most susceptible.
Employees are lured by curiosity, fear, and urgency — and phishing emails are increasingly well designed to blend into an inbox. If you don't properly train your employees to recognize and report suspicious emails, the above tools can be irrelevant. If you do, they can provide you with an array of options that are equally as advanced as your adversaries.
"If you don't properly train your employees to recognize and report suspicious emails, security tools won't be enough to protect you!"
Tweet This