TL;DR: Many PHP applications are still running on PHP 5.x, not ready to take full advantage of the awesome features that PHP 7 offers. A lot of developers have not made the switch because of certain fears of compatibility issues, migration challenges and the strange awkward feeling that migrating will take away a big chunk of their time. In this tutorial, you'll learn how to upgrade your PHP 5 application to PHP 7 starting from upgrading your development environment.
PHP 5 and PHP 7
PHP 5 has been around for a very long time, over 10 years now. In fact, many production PHP apps are currently running on either PHP 5.2, 5.3 or 5.6. PHP 5 brought a lot of awesome features to PHP such as:
- Robust Support for Object oriented programming.
- Standard PHP Library (SPL)
- Closures.
- Namespaces.
- Magical methods for metaprogramming.
- MySQLi - improved MySQL extension.
- Cleaner Error handling.
- Better support for XML extensions.
Unfortunately, every thing that has a beginning must have an end. PHP 5.6 active support ended January 19, 2017. It will receive security support until December 31, 2018.
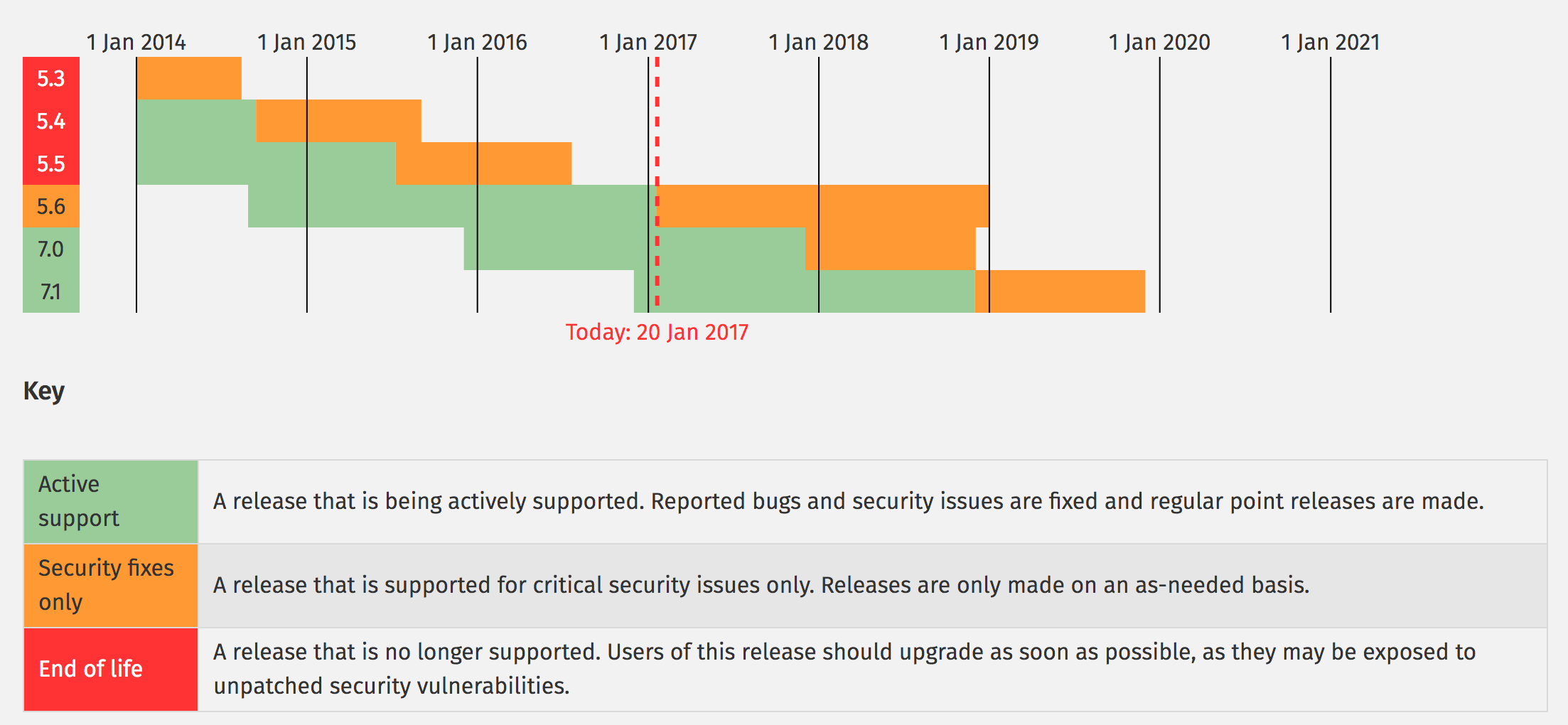
PHP 7.0 was officially released on December 3, 2015 with a lot of new features and better performance benefits. It is twice as fast as PHP 5. A summary of the new features are highlighted below:
- Return and Scalar type declarations
- Better Unicode support
- Null Coalescing Operator
- Fatal errors conversion to Exceptions
- Generator Enhancement
- Anonymous Classes
- Secure random number generator
- Removal of deprecated features
and much more! If you aren't using any of the deprecated features in your PHP 5 app, then the transition to PHP 7 will be seamless. In the next post, I'll give a very detailed rundown of PHP 7 features, including the deprecated features.
Upgrading your development environment to PHP 7
The first step to upgrading your application to use PHP 7 features is to migrate your development environment from PHP 5.x to PHP 7.x. We will cover how to upgrade your development environment to run PHP 7.x on Ubuntu, CentOs, Windows and Mac OS machines.
Mac OS X
If you are a fan of Homebrew, you can install PHP 7.0 via homebrew like so:
brew tap homebrew/dupes
brew tap homebrew/versions
brew tap homebrew/homebrew-php
brew unlink php56
brew install php70If you were using PHP 5.6, then you should unlink the old PHP by running
brew unlink php56else unlink whatever version is present before you go ahead to install PHP 7.0.
Another option is to install it via curl on your terminal like so:
curl -s https://php-osx.liip.ch/install.sh | bash -s 7.0Windows
If you are fan of WAMP or XAMPP, then you can just download the latest versions of the software. It comes packaged with PHP 7.0.
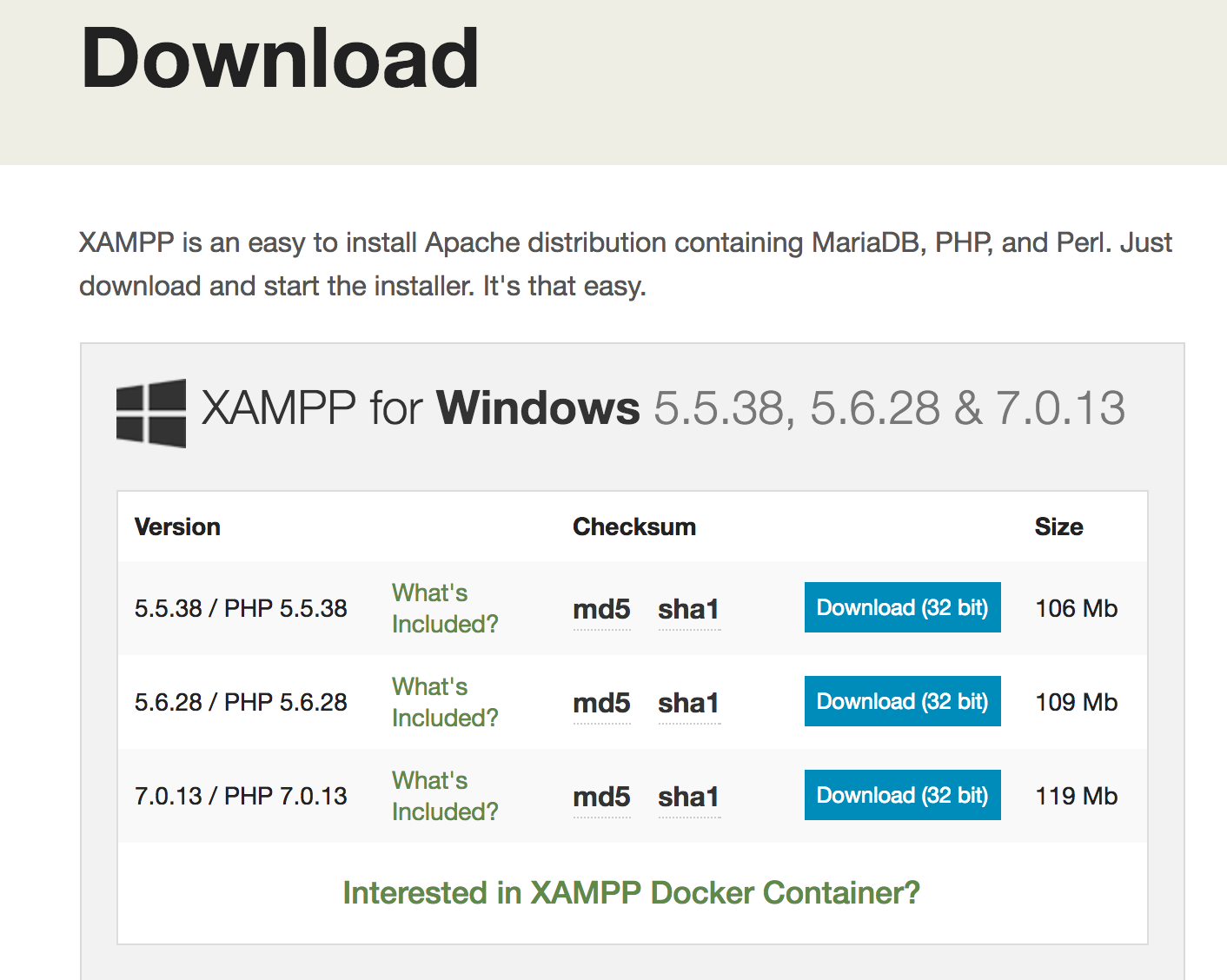
Another option is to download the PHP 7.0 distribution for windows from http://windows.php.net/download#php-7.0.
Ubuntu
If you are running Ubuntu on your machine, especially around v14 and 15, you can install PHP 7.0 by running these commands:
sudo apt-get update
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/php
sudo apt-get install -y php7.0-fpm php7.0-cli php7.0-curl php7.0-gd php7.0-intl php7.0-mysqlNote: You can check out how to install PHP 7 and Nginx here, and manually build memcached module for PHP 7.
Debian
If you are running Debian on your machine, especially around v6, v7 and v8, you can install PHP 7.0 by doing the following:
- Open up your
/etc/apt/sources.listfile, and make sure you have these commands below:
If you are using a Jessie distribution
deb http://packages.dotdeb.org jessie all
deb-src http://packages.dotdeb.org jessie allIf you are using a Wheezy distribution
deb http://packages.dotdeb.org wheezy all
deb-src http://packages.dotdeb.org wheezy all- Fetch and Install the GnuPG key
wget https://www.dotdeb.org/dotdeb.gpg
sudo apt-key add dotdeb.gpg- Install PHP 7.0
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install php7.0CentOS / Red Hat Enterprise Linux
If you are running CentOS or Red Hat Enterprise Linux operating system on your machine, you can install PHP 7.0 by running the following commands on your terminal like so:
sudo yum update
rpm -Uvh https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
rpm -Uvh https://mirror.webtatic.com/yum/el7/webtatic-release.rpm
sudo yum install php70w
sudo yum install php70w-mysqlWhen you are done, run this command php -v, you should see something like this:
PHP 7.0.0 (cli) (built: Dec 2 2015 20:42:32) ( NTS )
Copyright (c) 1997-2015 The PHP Group
Zend Engine v3.0.0, Copyright (c) 1998-2015 Zend Technologiesphpbrew
PHPBrew is a tool that you can use to build and install multiple versions of PHP on your machine. It can:
- Build PHP with different variants like PDO, MySQL, SQLite, debug etc
- Compile Apache PHP module and separate them by different versions.
- Switch versions very easily and is integrated with bash/zsh shell.
- Install & enable PHP extensions into current environment with ease.
- Install multiple PHP into system-wide environment.
- Detect path for Homebrew and MacPorts.
You can install it on your machine like so:
curl -L -O https://github.com/phpbrew/phpbrew/raw/master/phpbrew
chmod +x phpbrewThen you can install it into your bin folder like so:
sudo mv phpbrew /usr/local/bin/phpbrewNote: Make sure you have /usr/local/bin in your $PATH environment variable.
You can install PHP 7 by running the following commands:
phpbrew self-update
phpbrew install next as php-7.1.0
phpbrew use php-7.1.0You can use phpbrew to install PHP 7.0 from GitHub like so:
phpbrew install github:php/php-src@PHP-7.0 as php-7.0.0Most times, we use PHP with other extensions such as MySQL, PDO, OpenSSL etc. You can use phpbrew to build your PHP environment with various variants like so:
phpbrew install 7.0.0 +mysql+mcrypt+openssl+debug+sqliteThis command above will build PHP with MySQL, mycrypt, OpenSSL, debug and SQLite.
Vagrant
Vagrant provides a simple, elegant way to manage and provision Virtual Machines. The development environments that run on Vagrant are packaged via Vagrant boxes. Vagrant boxes are completely disposable. If something goes wrong, you can destroy and re-create the box in minutes! One of such boxes I recommend is Laravel Homestead.
Note: You can check out these awesome free courses on learning how to use Vagrant on https://serversforhackers.com
Laravel Homestead
Laravel Homestead is an official, pre-packaged Vagrant box that provides you a wonderful development environment without requiring you to install PHP, a web server, and any other server software on your local machine. Homestead runs on any Windows, Mac, or Linux system. It includes the following:
- Ubuntu 16.04
- Git
- PHP 7.1 (Latest version of PHP)
- Nginx
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- Sqlite3
- Postgres
- Composer
- Node (With Yarn, PM2, Bower, Grunt, and Gulp)
- Redis
- Memcached
Beanstalkd
Install VirtualBox 5.1, or VMWare, and Vagrant.
Now that you have Vagrant and VirtualBox or VMware installed, go ahead and download the Laravel Homestead box like so:
vagrant box add laravel/homesteadFollow the instructions on the Laravel Homestead documentation to find out more about the installation process.
I recommend Windows users to take a stab at using Laragon. It provides an alternative but suitable and powerful environment like Laravel Homestead.
php7dev
Another Vagrant image is php7dev by Rasmus Ledorf (Creator of PHP). It is a Debian 8 Vagrant image which is preconfigured for testing PHP apps and developing extensions across many versions of PHP. You can gloriously switch between PHP versions by using the newphp command.
Follow the instructions on the README to find out how to install, configure and use.
Valet
Valet is a PHP development environment for Mac minimalists. It was built by Taylor and Adam Wathan of the Laravel community. It is a fast blazing development environment that uses roughly 7MB of RAM. It requires Homebrew.
Laravel Valet configures Mac to use PHP's built-in web server in the background when your machine starts. With Valet, if you create a project folder called auth0-php, then you can just open auth0-php.dev in your browser and it will serve the contents of the folder automatically.
You can share whatever you are working on locally with someone in another part of the world by just running this command:
valet share
You can even serve a local site over encrypted TLS using HTTP/2 by invoking a command like so:
valet secure blogwhere blog is the name of the site or project folder. Valet generates a Fresh local TLS certificate.

Very awesome!
Out of the box, Valet supports Laravel, Lumen, Symfony, Zend, CakePHP 3, Wordpress, Bedrock, Craft, Statamic and Jigsaw. However, you can extend Valet with your own custom drivers.
Follow the instructions on the laravel valet documentation to find out how to install and get started using it.
Docker
php7-dockerized
php7-dockerized is a simple PHP 7 Docker and Compose environment that is bundled with Nginx and MySQL. Follow the instructions on setting up a local PHP 7 development environment with docker and compose!.
Laradock
Laradock is a docker PHP development environment that gives you a wonderful development environment without requiring you to install PHP 7, Nginx, MySQL, Redis, and any other software on your machines.
- Clone Laradock inside your project like so:
git clone https://github.com/Laradock/laradock.git- Enter the laradock folder and run this command:
docker-compose up -d nginx mysql redis beanstalkd- Open your
.envfile and set the following:
DB_HOST=mysql
REDIS_HOST=redis
QUEUE_HOST=beanstalkdFollow the instructions on the laradock documentation to find out how to install and configure it.
phpdocker
phpdocker.io is a PHP and Docker generated environment. It supports PHP 7 up until 7.1 beta. Follow the instructions to set it up like so:
- Clone https://github.com/phpdocker-io/phpdocker.io
- Copy
app/config/parameters.yml.distintoapp/config/parameters.yml - Run
composer install - Run
bower install - Run
php bin/console assets:install --symlink --relative - Run
docker-compose up -d
Don't hesitate to submit an issue on the phpdocker-io repo if you hit a roadblock.
Note: Chris Fidao has a fantastic course on Docker. With his course on shippingdocker.com, you'll learn how to use Docker in development, testing and production.
There are different ways of setting up a PHP 7 development environment. The few I have mentioned here should give you a lot of options in getting your machine ready to effectively test PHP 7 features.
Conclusion
We have successfully covered various ways of setting up a PHP 7 development environment. The first step to migrating an app from a specific language version to another is ensuring that the development environment supports the new version.
Looking for the best way to secure your PHP projects? Auth0 offers a generous free tier to get started with modern authentication. This modern tool provides the simplest and easiest to use User interface tools to help administrators manage user identities including password resets, creating and provisioning, blocking and deleting users.
Do you have other ways of setting up PHP 7 development environments? Are you currently using an awesome tool to run your PHP 7 apps? Please let me know in the comments section.
In the next article, we'll go through all the features of PHP 7 that you can leverage when migrating your PHP 5 application!





