With more people working remotely or online post-2020, the FBI reports that cybercriminals are quadrupling the number of cyberattacks they use to disrupt online activities. Research also shows the impact to organizations and their users from a single successful cyberattack is growing each year.
For example, in 2017, nearly 197 million records were exposed due to data breaches. In 2020, that number grew to 37 billion, even though the overall number of data breaches had decreased. And IBM reports that the costs are growing for organizations that fall victim to these attacks in countries like the United States, where the average cost of a data breach grew from $7.91M to $8.64M between 2018 and 2020.
Many of the methods cybercriminals use to breach organizations rely on human error. Even your sharpest employees can become your greatest weakness if they click on a malicious link without realizing it. However, other cyberattacks exploit gaps in your data security efforts to gain access to sensitive data.
Below are seven of the most common cyberattacks your organization will face in 2021 and the ways to protect yourself against the data breaches they have the potential to cause.
1. Malware Attacks
Malware refers to many different types of malicious software designed to infiltrate, spy on, or create a backdoor and control an organization’s systems or data. This includes ransomware, worms, trojans, adware, and spyware. Experts report that malware usage is up almost 800% since early 2020.
Malware has the potential to cause major data breaches and severely disrupt business operations. Microsoft was the victim of a major ransomware attack, where WannaCry took advantage of a weak spot in their operating system and displayed the following message to banks, health care providers, manufacturers, and other businesses across the globe:
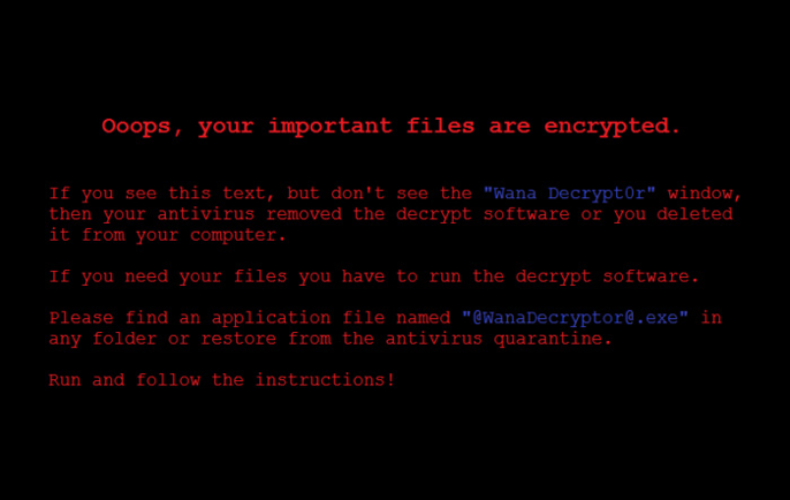
To regain access to their computers, along with any files that hadn’t been backed up, businesses had to pay a ransom to the creators of the WannaCry program in Bitcoin.
Malware is typically downloaded unwittingly by clicking a malicious link or by tricking a user into thinking they're downloading something legitimate when they’re not.
How to Protect Against Malware Attacks
Teaching your employees how to spot suspicious links and pop-ups that could contain malware will help reduce the chance that it could infect your systems.
Additional ways to protect against malware include keeping your operating systems up to date to ensure known security gaps are patched and using anti-virus software. For example, the Equifax data breach could have been prevented had a known patch been installed in time.
2. Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks attempt to steal information from users or trick them into downloading malware by sending malicious emails or text messages (SMS) that look like real requests but are, in fact, a Scam. Here’s a Dropbox email asking users to verify their email address that’s actually a phishing attack:
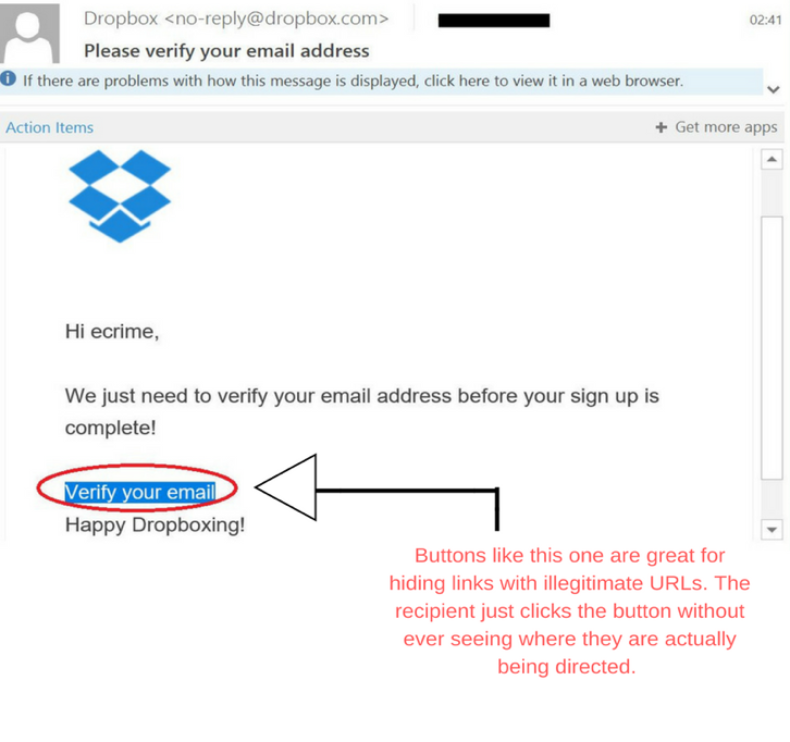
According to Verizon’s 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report, phishing attacks are the most common cause of data breaches globally and have been the root cause of notable instances of cybercrime in the last decade.
The cybercriminals who breached the AP News Twitter account and falsely tweeted that the White House was under attack used a targeted phishing attack (spear-phishing) to gain access to the account, as did the bad actors who leaked sensitive emails from Hillary Clinton’s campaign chairman before the 2016 election.
How to Protect Against Phishing Attacks
The best way to protect your organization against phishing attacks is to educate your employees on how to spot a questionable email or text message. The training programs below can help you do this:
- Digital Defense’s SecurED training program
- Inspired eLearning’s Security Awareness
Additionally, CSO has compiled a list of resources that can help you train your teams to spot phishing attacks here.
3. Distributed Denial of Service Attacks
Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks disrupt the traffic to a website, application, server, service, or network by overwhelming it with a flood of traffic from compromised computer networks (botnets) that prevents real users from accessing it. In 2018, GitHub experienced the largest DDoS attack ever when it was hit with 1.35 terabits of traffic per second and was offline for almost 20 minutes as a result.
DDoS attacks are common and increased by 50% in 2020 compared to 2019, with a large surge occurring in early 2020 during the pandemic, according to security company Kaspersky.
How to Protect Against DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks are tricky to identify because they’re often hard to distinguish from legitimate traffic. Some methods of protecting against DDoS attacks include blocking all traffic for a short period of time, rate-limiting traffic to a website, using a web application firewall to detect suspicious traffic patterns, or scattering traffic across a network of servers to reduce the attack’s impact.
4. Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks are when bad actors spy on or intercept communication between you and your users or employees. MitM attacks are most commonly used to steal personal or company information or to redirect that information to another destination or in espionage situations, such as when Russian hackers attempted to breach the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW).
MitM attacks are not the most common cyberattack because many of the same objectives can be achieved using malware. However, MitM attacks do present a threat for organizations because they’re often hard to spot and because more employees are working remotely post-2020.
For example, fake WiFi networks are easy to deploy in public places like coffee shops where remote employees often work. People often connect to these networks without realizing it, allowing bad actors to spy on them while they use the network.
How to Protect Against MitM Attacks
End-to-end encryption protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS) are the best way to protect against MitM attacks. Additionally, requiring your employees to use a VPN to access company networks over public WiFi will ensure that any information shared during their session remains private, regardless of whether the network belongs to a bad actor or if their coffee shop’s WiFi is simply unsecured.
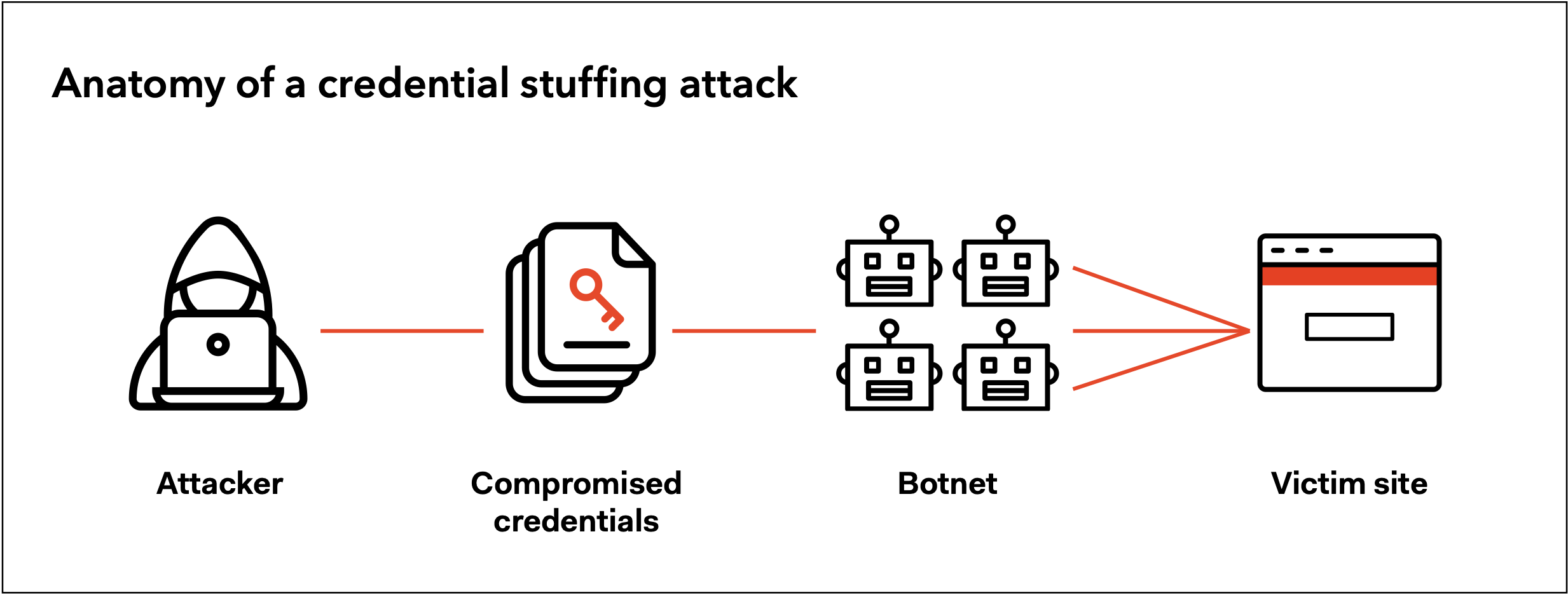
5. Credential Stuffing Attacks
Credential stuffing is a type of brute-force cyber-attack where bad actors use stolen usernames and passwords from one data breach to access user accounts at another organization.
Credential stuffing is possible because, statistically, 65% of all people reuse the same password across multiple accounts. As a result, credential stuffing attacks are one of the most common causes of data breaches globally.
How to Protect Against Credential Stuffing Attacks
The best way to protect against credential stuffing attacks is by either implementing passwordless authentication or multi-factor authentication (MFA). Passwordless authentication prevents bad actors from using stolen credentials by eliminating them altogether, while MFA requires bad actors to verify their identity in one or more ways in addition to the stolen credentials they’re using to log in.
6. Password Spraying Attacks
Password spraying is also a type of brute-force attack where bad actors attempt to guess a user’s password from a list of common passwords like “123456” or “password.”
Like credential stuffing, password spraying is quite common. For example, Verizon’s 2020 Data Breach Report showed that over 80% of all hacking-related data breaches involved brute-force methods like password spraying.
How to Protect Against Password Spraying Attacks
Password spraying attacks can be prevented by using passwordless authentication or MFA, just like credential stuffing attacks can be. However, you can also reduce the risk and impact of a data breach via password spraying by following the NIST Password Guidelines, which are considered the best password standards in the world.
7. Mobile Device Attacks
Many organizations are working to increase the mobility of their workforce because it improves operational efficiency and productivity. However, cybercriminals are well aware of this fact and are targeting mobile devices more frequently year over year with a variety of attacks on this list, which puts organizations at risk for a data breach through more devices than before.
The Pegasus attack on Apple’s iOS software is a prime example. Pegasus infected iPhones through phishing text messages that asked recipients to click on a link inside the text message. Clicking the link triggered the installation of spyware capable of monitoring people through their camera and microphone. And once infected, users had their login credentials stolen from WhatsApp, Gmail, and other sensitive communication applications.
How to Protect Against Mobile Device Attacks
Protecting your organization against mobile security threats requires a strong enterprise mobility management (EMM) program, as well as mobile device management (MDM) tools that help you protect any company data that may be on your employees’ personal or work devices. Identity and access management tools like multi-factor authentication can also help secure any work applications that contain sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Create Additional Layers of Security at the Login Stage
The impact of many cyberattacks on this list (as well as others that many companies face) can be mitigated or prevented with strong authentication protocols.
First and foremost, this means good password policies and sound employee education. However, taking the next step to secure login procedures with security functionality like multi-factor authentication, brute-force protection, or passwordless authentication can add a new dimension of safety to your system.
Auth0 makes it easy to build secure authentication for the right people without compromising on user experience — learn more about Auth0’s platform here.
About Auth0
Auth0 by Okta takes a modern approach to customer identity and enables organizations to provide secure access to any application, for any user. Auth0 is a highly customizable platform that is as simple as development teams want, and as flexible as they need. Safeguarding billions of login transactions each month, Auth0 delivers convenience, privacy, and security so customers can focus on innovation. For more information, visit https://auth0.com.